What is a Business Model?
What is a Business Model?
A business model is the foundation of a company that outlines how the business will generate value.
While a business model can be defined in very simple terms, the history, evolution, and hundreds of variations add immense complexity to the topic. Therefore, business owners, operators, and future entrepreneurs need to continue evolving their understanding of the business model to be successful.
We've created this post to take a deep dive into what is a business model using examples from past and current successful companies.
Breaking the boundaries of the business world
Before the widespread access to the internet, most business owners based their models on catering to a localized market. However, few companies had the capital to serve consumers globally, limiting the flexibility of their business model.
Once the internet became accessible, everything changed. Digitalization of the economy offers infinite potential for innovation.
In the 1990s, internet-based companies seemed to be on a trajectory of infinite growth until the dot com bubble burst, bankrupting hundreds of businesses. However, companies that were able to shift their model, such as Amazon, eBay, and Priceline, survived the crash.
Today we are witnessing another shift due to policy and changes in spending patterns created by the COVID-19 pandemic. As the economy becomes increasingly digital, companies must continue innovating and adapting to customer trends to survive.
The Emergence of the Lean Start-Up
After the dot com bubble, the companies that did survive expanded at a rate never seen before. As a result, more entrepreneurs entered the technology space with hopes of rapid growth. As a result, the startup business model grew in popularity, centering around the lean methodology that includes continuous innovation and built-in loops that react to customer feedback.
PayPal and Dropbox are among the best examples of the lean startup model replicated by hundreds of companies in the early 2000s. Both began as simple, innovative online services and have since expanded user adoption and value offerings.
Customer obsession dominates tech
One of the primary aspects attributing to the success of the lean startup model is the ability to adapt to customer feedback. Customer obsession refers to an organization that constantly seeks input from consumers and continuously improves the customer experience.
Amazon's #1 leadership principle is to collect data to gain a deep understanding of the customer's wants and needs, then adapt the model to accommodate its users. Customer obsession is a fundamental component of modern technology companies because the lean model and access to data have allowed operators to adapt to the market quickly. If you aren't learning from the customer, a competitor will inevitably find a competitive advantage.
What is a business model, and why is it important?
A business's model is at the center of how the company operates, adapts to new revenue streams, broadens its customer base, and retains revenue.
The scalability allowed by the internet makes the business model more important than ever. Companies can introduce exciting new ideas, ways to reach consumers, and add value through the company's framework.
A quick history of business models
Throughout history, businesses have always followed a model. One of the earliest examples is from the early 20th century; the 'bait and hook' or 'razor and blades' model includes offering a basic product at a loss and then recovering the loss through reoccurring payments or supplemental products.
Dollar Shave Club has developed the modern version of the razor and blades model by literally selling razors and other high-end shaving products. We did a full breakdown of the company and model in our blog; check out the article for more information.
The franchise is one of the most prominent models to gain popularity before the dot com bubble. McDonald's, Ikea, and Ryanair are excellent examples of how retail businesses can be replicated all over the world once the model is validated.
Read: A SWOT Analysis of the Furniture Giant: What are the Strengths of IKEA
Why A business model is not a business plan
Many inexperienced entrepreneurs confuse the term business model with a business plan. The major difference is in the specific structure.
A business plan is a document that thoroughly explains a business's goals and how the organization will meet those metrics over time. Critical aspects of a business plan include:
Business description and summary
Market analysis
Competition overview
Operating plan
Product/services descriptions
Marketing strategy
A business model is a more broad, less concise term consisting of how the organization will reach consumers without a direct plan for financing, revenue growth, operations, or marketing.
Difference between a business model and business plan
If we look at the McDonald's franchise business model, we can observe the difference between the model and the plan.
McDonald's franchises restaurants to business owners worldwide to capture market share and continue to grow. The franchise owner pays an upfront fee along with revenue sharing and, in turn, gains access to branding, supply chain, operations procedures, and other essential aspects of the business.
A McDonald's business plan would be the document presented by the prospective franchisee owner to outline how they would become economically viable in a specific market. The plan would include plans for a location, financing, hiring procedures, management structure, employee compensation, and other variables that would be unique to their specific restaurant.
A business model is not a revenue generation strategy
Another misconception is that a business model is strictly a revenue generation or monetization strategy. While how a company creates profit and plans to continue to grow are critical components of a viable business model, it is one aspect of a larger strategy.
Is a business model a business strategy?
A business strategy is a plan that outlines how a company will compete in a specific market. Companies typically create a general overview of marketing, operational, and financial strategies.

Business models differentiate from a business strategy because a model is less in-depth. Harvard Business School's Clay Christensen suggests that a business model should consist of four elements:
Customer value proposition
Profit formula
Key resources
Key processes
A business model should include the elements; however, it doesn't require an analysis of each component of the model.
Why business models matter?
The business model is the foundation for every company, outlining how the enterprise will navigate and deliver value in a market.
TikTok, the increasingly popular Chinese social media platform, utilizes a prosumer business model. The company focuses on keeping users engaged by creating a stimulating user experience, but the app doesn't produce videos. Instead, TikTok relies on user-generated content to populate the feed and provides the technology to encourage engagement.
The business model is at the center of TikTok's success. Developers focus on improving the social media experience with content creation technology and an algorithm that offers nearly every user the opportunity to go viral.
Why are business models important?
TikTok's business model is important because it separates the platform from other social media companies. For example, Facebook and Instagram moved away from catering to the individual and focused on creating revenue through brands spending on paid advertising. TikTok's model empowers the common user through the algorithm and innovative tools to help videos go viral.
The importance of business model design
Business model design defines an organization's logical rationale for implementing business strategy. For example, Dropbox started as a simple application that gave everyday users access to cloud storage. Once the startup proved its dominance of the niche, the model shifted to include more services such as eSignatures, document transfers, device backup, and the ability to sell digital products directly from Dropbox.
The lean design with a foundation centered around cloud computing allows Dropbox to continue to innovate and bring new services to market.
Business modeling is about experimentation
A new business model is similar to a hypothesis. An entrepreneur comes up with an idea and tests the business in the market like a scientist tests and validates a theory with research.
Apple is the perfect example of a company that benefited immensely because of experimentation and continues to do so. In the 1990s, Apple's business model focused on producing personal computers. Then, in 2007, Steve Jobs famously introduced the iPhone.
No one knew if a highly intuitive cell phone would meet the market's needs. Obviously, the market welcomed the idea, and the experiment was validated. Apple's rival, Microsoft, had to play catchup in the emerging smartphone sector and eventually discontinued its Windows phone in early 2016.
In January 2022, Apple became the first company to surpass a 3 trillion-dollar market capitalization.
Technological innovation vs. business model innovation
Companies like Apple continue to innovate the business model and deliver new products with added value. Tesla is another example of a company that has profited immensely from technological and business model innovation.

How Tesla benefits from technological innovation
Before the Tesla Roadster, the electric vehicle was virtually dead. However, once Tesla revolutionized large battery technology, EVs could drive further on one charge reducing range anxiety and becoming more practical for consumers.
Incorporating large batteries and improving energy utilization is an example of technological innovation. While enhancing the tech is a central piece of why Tesla has become so successful, it isn't the way the battery/software/EV company is beating out competitors.
Telsa's genius business model innovation
The rise of Tesla has not only changed how cars use energy but also how cars are sold. Instead of manufacturing thousands of vehicles, parking them at a dealership, and giving salespeople a commission on every car sold, Tesla implemented a D2C model. Consumers can choose and order their car online; once it is built, it is delivered directly to their doorstep.
Another example is Tesla's charging infrastructure. While the Superchargers are technological innovation, the idea to build chargers across continents, even in desolate, rural areas without a Tesla owner for hundreds of miles, is an example of business model innovation.
Read: An Excerpt From The Car Manufacturer's Business Model Canvas: Tesla
Why business model innovation matters so much
Change in consumer habits is inevitable. Policy, social issues, trends, and technology are constantly changing, making business model innovation and the ability for companies to adapt to the market incredibly important.
Let's go back to social media as an example of why business model innovation matters. In early 2010, Facebook seemed to have control over the market; however, the platform stopped implementing new technology to keep users engaged.
Instagram was launched in 2010, followed by Snapchat in 2011, taking significant market share from FB, especially in crucial, younger demographics. As a response, Facebook acquired Instagram and released IG and FB stories along with selfie filters in response to Snapchat.
For the next 5 years, Facebook, now known as Meta, regained control over the market thanks to the IG acquisition. But the tech company failed to recognize the value of short, user-generated video content. While users could upload a video to FB and IG, the platforms didn't provide the tools to create unique videos directly from their phones.
The failure to innovate welcomed a new player into the social media space. Today, TikTok surpasses 1 billion monthly users, still less than FB and IG but is growing at a much faster rate than the Meta-operated platforms.
Competitive moats are generated around business model innovation
Warren Buffet believes the "most important" factor when choosing a viable investment is the durability of a "competitive moat." The term refers to the company's competitive advantage in a market and the ability to retain the advantage long term.
When a new technology, like the internet, becomes accessible to consumers, novel business models will inevitably emerge. One of the most relevant is Netflix. The streaming company took advantage of high-speed internet in consumers' homes across the world.
After pivoting to streaming, Netflix maintained its competitive moat for over a decade. Even after other companies entered the space, Netflix invested in original content that kept users satisfied.
After Netflix reported losing over 200,000 subscribers in the first quarter of 2022 and over a million in Q2, the stock plunged nearly 40%. The news was a bombshell and signaled that Netflix's once seemingly impenetrable moat was dramatically weakened.
While Netflix's decline may have been inevitable, Google gives us an excellent example of creating a competitive moat with longevity. As of June 2021, 92.47% of all internet searches have been conducted through Google, showing complete dominance over the market.
Google's early understanding of the web, investment in infrastructure worldwide, and continuous access to an unfathomable amount of user data provide a truly impenetrable moat.
Business model innovation as a traction model
An essential aspect of a modern business is receiving feedback and making changes on the fly. Companies like Amazon and PayPal survived the dot com bubble because they could find the most profitable business model market fit. Both companies started with very different business models than how they are positioned in the market today. The rise of lean startups is due to the model's flexibility to receive customer feedback and make quick adjustments to stay competitive.
Jack Dorsey's company Block consisting of Square, Cash App, Spiral, and Tidal, offers an excellent example of an organization that utilizes the traction model.
Square began as one of many online payment processing companies. The model evolved to integrate seamlessly with eCommerce brands as well as brick and mortar retailers. Dorsey's vision for online payments grew to include person-to-person transactions with Cash App.
The billionaire tech entrepreneur continues to innovate as his businesses fit their market fit and gain traction. Cash App has grown to offer consumers the ability to purchase stocks and cryptocurrency.
As the technology sector evolves, blockchain and the metaverse appear to be the next emerging components with massive potential. Block is in an ideal position to capitalize on the shift in the space through financial technology with Square, Cash App, and Spiral. In addition, Tidal offers an exciting opportunity to leverage decentralized ownership on streaming platforms. Financial services and digital content will be two critical components of metaverse technologies.
Check out our article The 7 Metaverse Opportunities You Shouldn't Miss for more on the exciting new technology.
Dorsey demonstrates he understands a flexible business model is needed to survive. Once his companies find their market fit, he expands, the perfect example and execution of the traction model.
What are the primary components of a business model?
As mentioned, business models are highly diverse and continuously changing in reaction to the market. However, a business model's primary components demonstrate commonalities among successful examples. The business model canvas is a framework for visualizing and structuring models created in the 2008 book Business Model Generation by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur.
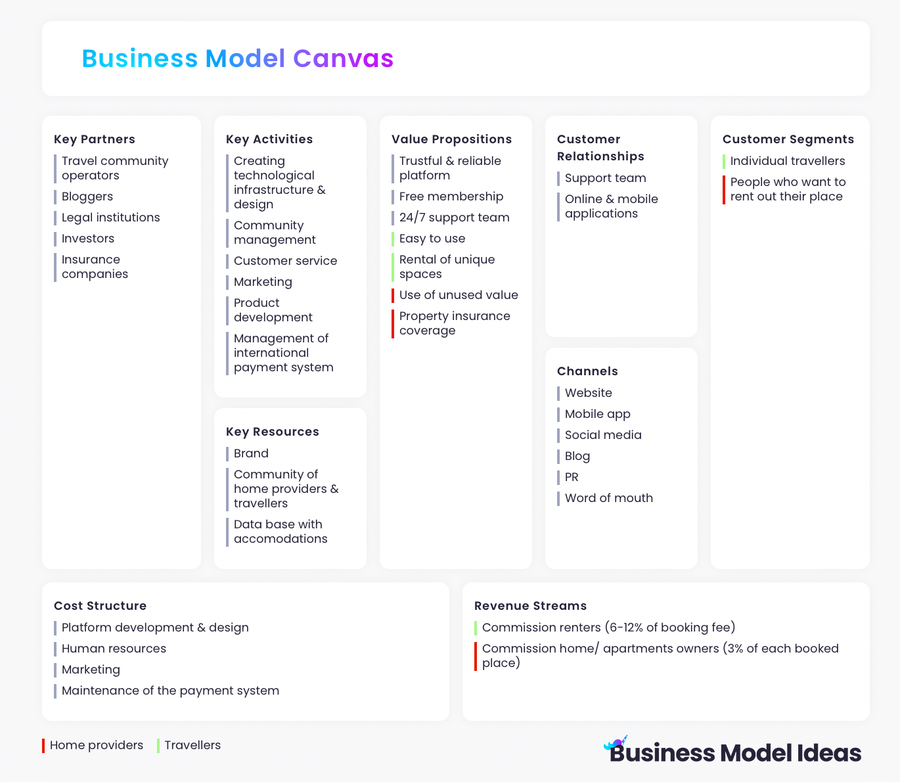
Below are the nine building blocks and a brief explanation of every successful business model according to the business model canvas.
Key Partners – Suppliers that offer strategic relevance to the business model.
Value Proposition - "Think of the Value Proposition as a contract between the customer and your company where the customer 'hires' your company to solve a problem." Clayton Christensen
Customer Segments – A business's customers and target groups
Cost Structure – Significant cost blocks and structures.
Revenue Streams – All methods of generating revenue.
Key Activities – Operations essential for growth
Customer Relationships – Maintaining customers rather than paying exponentially more to acquire new consumers.
Key Resources – Aspects of the model that are crucial for success (employees, technology, patents, facilities, etc.).
Channels – HOW customers are reached and how they purchase products in the market.
The business model canvas perspective
The business model canvas offers structure and encourages collaboration to an abstract concept. Laying out the building blocks tangibly exposes flaws and helps teams understand the model on a high level.
If you are interested in learning more about the concept, read our blog post, Business Model Canvas Compact – Structure, Explanation, and Examples. Here we cover each component of the business model in-depth and how to use the business model canvas to analyze and develop your business model.
The business model navigator perspective
Another popular method to analyze business models is the business model navigator. The concept was invented at the University of St. Gallen in Switzerland and focuses on innovating business models rather than just products and services.
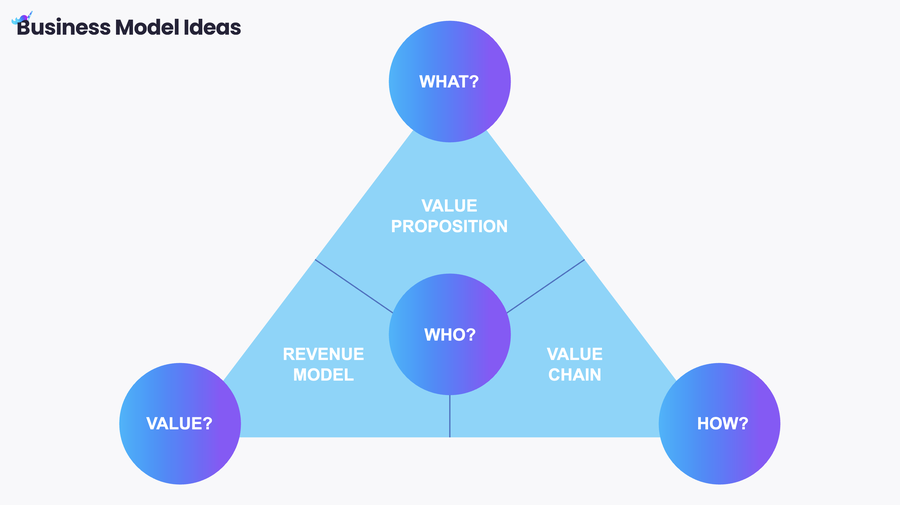
The business model navigator offers a meta-perspective broken down into 4 questions:
Who are the target customers?
What is the benefit?
How is the benefit created and delivered?
How does the company earn money?
St. Gallen's business model navigator is less detailed than the business model canvas and is often used as a starting place when formulating or analyzing models.
The mix of both worlds
Answering the questions outlined by the business model navigator directly answers the most important aspects of the model and how what areas need to be innovated. As a result, the business model canvas is a much more thorough examination.
We suggest utilizing both frameworks starting with navigation. Once you've determined the fundamentals of your business model, a complete analysis with the business model canvas should be conducted.
Remember that a successful business model needs to be positioned to adapt and innovate. The most profitable organizations, especially since the internet, continue to demonstrate the ability to pivot based on feedback from the market.
How many types of business models exist?
Narrowing down an exact number of business models is impossible but for us there are 108 patterns. New models are being tested every year, and old models evolve in real-time.
In addition, most companies don't fit just one type of model. For instance, the streaming app Spotify applies multiple business model patterns, including freemium, accessibility, and mass customization.
While Spotify is the largest music streaming service with a market share of over 30%, the company continues to innovate its business model. In the past 5 years, Spotify has shifted its focus on podcasting and secured some of the largest shows through exclusive licensing deals.
There are hundreds of business model patterns and new ones emerging every year. The important takeaway is not the amount but the need for models to adapt and innovate.
Vision vs. mission: why understanding the difference between them is important
While a business model and the company's mission are constantly changing, the vision rarely changes course.
To understand the difference between the two types of business statements, let's look at Spotify.
Spotify's Vision Statement:
"We envision a cultural platform where professional creators can break free of their medium's constraints and where everyone can enjoy an immersive artistic experience that enables us to empathize with each other and to feel part of a greater whole."
Spotify's Mission Statement:
"Unlock the potential of human creativity by giving a million creative artists the opportunity to live off their art and billions of fans the opportunity to enjoy and be inspired by these creators."
We see how the vision statement describes Spotify's goals for the future, and the mission statement outlines how the streaming platform conducts business.
The vision focuses on more broad elements like culture, constraints of a medium, and the artistic experience. Spotify's mission statement is more focused on the opportunity for the individual artist and the fan's experience.
Spotify's recent moves into licensing demonstrate the mission statement by allowing artists to live off their art but still align with the broader goal of unlocking the potential of human creativity.
Business model examples
Business Model Ideas features over 150 hand-picked business models from the most successful companies in the world. Our experts offer a complete breakdown of each model, including:
Company background information
Website link and social media handles
In-depth expert insights
Marketing analysis
To give you an idea of what Business Model Ideas offers, we've included three short case studies below from companies featured in our database.
Only Fans Business Model

Only Fans is an online platform that allows content creators to monetize their content. Creators set a subscription price to view their content and offer add-ons for additional fees. Only Fans keep 20% of the revenue, allowing influencers to profit from their online following without partnering with brands.
The rise of the social media influencer paved the way for Only Fans. Instagram, Facebook, and Snapchat users accumulated an incredible number of followers in short periods but weren't earning revenue directly from the social media companies. As a result, influencers were forced to partner with brands to monetize their followings.
Only Fans capitalized on the opportunity by offering influencers a place to monetize adult content. The platform leverages content creators and profits from their communities.
The Only Fans business model is highly innovative. Other social media platforms rely on advertising rather than users paying a subscription fee as the primary revenue source. While Only Fans is known for adult content, some creators use the platform to release exclusive content not available on their other social media channels.
The most prominent example is Cardi B. After the prevalent New York recording artist joined the platform, her account skyrocketed, earning the artist over nearly 10 million USD per month.
Digitalization due to the COVID-19 helped Only Fans grow significantly over the past few years. At the end of 2021, Only Fans had over 170 million registered users. Platforms like Only Fans and Patreon, with business models that empower the creator through the subscription model, could be the future of online content.
HBO Business Model

While Only Fans shows us a completely novel business model only made possible out of the evolution of the internet, HBO has been around since 1972.
Before the internet, HBO revolutionized how consumers viewed video content by pioneering the concept of premium content. After decades of dominance due to continuously producing high-quality programming, streaming changed the game.
HBO missed the initial rise of streaming content and was dramatically affected by Netflix being first-to-market. However, after an unsuccessful effort at streaming with HBO GO and the rebrand of HBO Max, the legacy premium cable company has regained dominance in the TV and movie production industry.
Releasing premium content has always been at the heart of HBO's business model; however, the rise of streaming has reshaped the company. Before HBO Max, the premium cable provider was primarily known for producing quality television. After witnessing Netflix build a production studio from nothing and releasing its own content exclusively on its platform, HBO shifted its business model, expanding to producing and releasing blockbuster films.
In 2022, Netflix is bleeding subscribers primarily due to HBO's ability to adjust its business model and capitalize on new consumer trends.
Roblox Business Model
Roblox is a global game creation platform that allows users to program and play games created by other users. Players can play existing games or create their own without limitations while collaborating with other Roblox users through various chat functions.
The platform is far from just another online game with an expansive, interactive map. Roblox game designers can generate income from the games they create through the platform's digital currency, Roblux.
Roblox's success is thanks to its innovative business model. Instead of creating another online game, Roblox designers built new technology that birthed a loyal community. With new gaming abilities and an opportunity to generate revenue on the platform, Roblox users are some of the most passionate users in the gaming community.
For many people, Roblox is a realistic view of what the so-called "metaverse" will actually look like. While Meta is dumping billions into creating VR, Roblox is revolutionizing existing technologies and empowering users.
Many business models becoming increasingly popular center around the user. Roblox is just one example of how Amazon's attention to consumer feedback has evolved. The next evolution of the consumer-obsessed lean startup focuses on giving users the tools to create and monetize content.
Reverse engineer any business model
Identifying areas that can be improved is difficult once a business is operational. Reverse engineering or conducting business analysis is an excellent method to expose areas that can be optimized or identify opportunities for innovation.
Business Model Ideas helps entrepreneurs and business operators learn from successful companies and implement similar methods into their models. As we've mentioned in the article, even the most prominent companies fail to understand the market and capitalize on new opportunities.
Conducting regular business analysis is a necessary practice for every organization.
Key takeaways for developing a successful business model
Innovation has always been at the center of developing a successful business model, but today it is critical due to rapid digitalization. New technologies are emerging overnight, offering opportunities for entrepreneurs to capitalize.
You don't need to revolutionize the automobile or build a digital online gaming world to create a successful business model. However, your model needs to be structured to adapt and capitalize on consumer feedback and changes in the market.
Key topics we covered
Digitalization of the economy and the rise of the lean startup
Amazon's customer obsession and dedication to reacting to consumer feedback
A business model is not a business plan or a revenue generation strategy
The importance of business model design
Experimentation is central to business modeling
Technology innovation is separate from business model innovation
The importance of competitive moats
Identifying opportunities for innovation and the traction model
Utilizing the business model canvas and business model navigator perspective
The difference between a vision and mission statement
List of 108 business models (from Business Model Ideas)
1 Asses > Multiple Businesses Business Model
1 Asset > Multiple Customer Segments Business Model
Accessibility Business Model
Add-On (Extras) Business Model
Advertising Business Model
Affiliation Business Model
Aikido Business Model
Auction Business Model
Barter Business Model
Cash Mashine Business Model
Circular Economy Business Model
Collaborative Consumption Business Model
Collaborative Production Business Model
Commision Business Model
Community Business Model
Complementary Offerings Business Model
Convenience Business Model
Cost Reduction / Affordability Business Model
Crowdfunding Business Model
Crowdsourcing Business Model
Customer Initimacy Business Model
Customer Loyality Business Model
Customization Business Model
Desegmented Business Model
Design Business Model
Digitalization Business Model
Direct Selling Business Model
Distribution Business Model
Do-it-yourself Business Model
Donation Business Model
Dynamic Pricing Business Model
Ease of Use Business Model
E-Commerce Business Model
Efficiency Business Model
Emotions (Image) Business Model
Experience Selling Business Model
Features Business Model
Fixed Prices Business Model
Flate Rate Business Model
Franchise Business Model
Free Business Model
Freemium Business Model
From Fixed to Variable Costs Business Model
Frugal Innovation Business Model
Gamification Business Model
Getting Things Done Business Model
Guranteed Availability Business Model
Hidden Revenue Business Model
Horizontal Expertise Business Model
Indirect Selling Business Model
Ingredient Branding Business Model
Integrator Business Model
Layer Player Business Model
Least Satisfied Business Model
Leverage Existing Customers Business Model
Licensing Business Model
Lock-In Business Model
Long Tail Business Model
Marginal Costs Business Model
Mass Customization Business Model
Mass Market Business Model
Most Profitable Business Model
Most Satisfied Business Model
Multi-Channel Business Model
Multisided Platform Business Model
New / Different Acitivities Business Model
New / Different Links Between Activities Business Model
Niche Market Business Model
No Frills Business Model
Non-Customers Business Model
Novelty Business Model
Object as Point-Of-Sale Business Model
Object Self Service Business Model
Open Source Business Model
Orchestrator Business Model
Outsourcing / Insourcing Business Model
Ownership vs. Access Business Model
Pay-per-Use Business Model
Pay What You Want Business Model
Peer-to-Peer Business Model
Performance Business Model
Performance-Based-Payment Business Model
Price Business Model
Product as a Service Business Model
Prosumer Business Model
Razor and Blade Business Model
Rent Instead of Buy Business Model
Revenue before cost Business Model
Revenue Sharing Business Model
Reverse Engineering Business Model
Risk Reduction Business Model
Sales Business Model
Segemented Business Model
Self-Service Business Model
Sensor as a Service Business Model
Service as Product Business Model
Shop-in-Shop Business Model
Solution Provider Business Model
Sponsoring Business Model
Subscription / Memebership Business Model
Supermarket Business Model
Sustainability Business Model
Ultimate Luxury Business Model
Unbundling / Bundling Business Model
User Designed Business Model
Vertical Integration Business Model
Virtualization Business Model
White Label Business Model
Business models examples infographic
Browse 150+ models at business model ideas
We believe that there is an immense amount of knowledge to be learned from existing business models. Entrepreneurs, operators, owners, and influencers can benefit from reviewing business models from the past and present to understand what has worked and where companies have missed opportunities.
At Business Model Ideas, we collect critical information on over 150 companies describing how they are positioned in the market. Our subscribers have access to a full business model canvas, patterns, SWOT analysis, expert insights, and marketing analysis for every company in our database.
Visit Business Model Ideas today for more information on our platform, and feel free to reach out if you have any questions.
Business models FAQs
What is a business model?
A business model defines how a company will offer value to its target market. The process of creating and modifying is called business model innovation and is essential to the success of an organization.
What is a business plan?
A business plan differs from a business model. The plan is a document that defines how a business will achieve its goals and offers a prediction for future growth.
The difference between a business model and a plan is the model provides the foundation for the company, whereas the plan describes the structure.
What is a business model example?
Below are three business model patterns from business model ideas:
Freemium model – The business offers services for free but requires payment for additional value. Many SaaS and online companies provide a free and paid version of their services. LinkedIn, Tinder, Skype, and Spotify are examples of a freemium model.
Franchise model – A successful business can offer the model to other operators for a fee. Franchise owners gain access to essential aspects of the business such as branding, advertising, operations, structure, and equipment. McDonald's, Burger King, and ScribeAmerica are all examples of the franchise model.
Circular Economy – Businesses that use product materials by recycling or repurposing materials. The materials have a much longer lifespan and help the company reduce waste. Freitag, Living Packets, and On Running utilize a circular economy business model.
What is a business model canvas?
The business model canvas is a framework for visualizing and structuring models created in the 2008 book Business Model Generation by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur.
Creating a business model canvas includes grouping key aspects of a business into 9 categories.
The practice involves building out a visualization encouraging collaboration and helping identify areas needing improvement.
What are the 9 building blocks of a business model canvas?
The 9 building blocks or categories in a business model canvas are customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
What is business model navigator?
The business model navigator is a simplified framework to develop business models created by the research institute at the University of St. Gallen in Switzerland. The framework consists of 4 questions to help develop models, identify existing problems, and encourage innovation.
What are the questions used in the business model navigator?
A business model navigator consists of 4 questions:
Who are the target customers?
What is the benefit?
How is the benefit created and delivered?
How does the company earn money?
What is the importance of a business model?
Business models are important because they offer the foundation for how a company reaches customers in a market. Understanding an organization's business model helps develop a value proposition. A continued realization of the model will encourage innovation and help the business adapt to the market.
At Business Model Ideas, we believe every business can benefit from business model analysis. We provide over 150 business models so business owners and operators can learn from other companies and apply elements to their models.
What is business model innovation?
Business model innovation is continuing to enhance a model and increase its value in the market. Successful businesses demonstrate the ability to evolve the value proposition and the mechanism of reaching consumers.
What is the difference between a vision and mission statement?
A vision statement is a passionate declaration of how a company wants to be positioned and viewed. Vision statements are typically idealistic and emotional.
Mission statements describe the products, services, or platform a company provides while outlining the organization's values and reason for existing.
A vision statement and mission statement are similar concepts and can even have overlapping elements. The main difference is a vision statement focuses on the future, whereas a mission statement describes the company's position today.
While mission statements are often changed or tweaked, the vision rarely differs.
Visit Business Model Ideas for more information on specific business models, patterns, and expert analysis.